Ultimate Guide: Healthy Cooking Oils Exposed for Vitality & Keto Success

Welcome to the journey towards healthier cooking! The oils we choose play a pivotal role in our well-being. Let's embark on a journey to understand which oils are best for your health and why making informed choices matters.
I. Choosing the Right Oil for Healthier Cooking
What's the Healthiest Oil for Your Kitchen?
In the world of oils, coconut, olive, and avocado oils stand tall as health heroes. Their unique properties not only add flavor but also offer significant health benefits. Coconut oil brings a tropical touch and medium-chain fatty acids that aid in metabolism. Olive oil, a cornerstone of the Ketogenic diet, boasts antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties. Avocado oil, rich in monounsaturated fats, supports heart health.
Understanding: Why Vegetable Oil Isn't Always Best
Despite its common use, vegetable oil might not be your healthiest option. Often refined and high in inflammatory linoleic acid, it's linked to increased inflammation and metabolic disorders. This inflammation can trigger various health issues, making it crucial to reconsider its usage.
Why Olive Oil Shines in the Healthy Oils Lineup
Olive oil takes the spotlight for its remarkable health benefits. Its abundance of monounsaturated fats and antioxidants(*) not only aids in reducing inflammation but also supports heart health and combats oxidative stress (*). Incorporating it into your cooking can be a delicious step towards a healthier you.
II. Spotting Unhealthy Cooking Oils
Which Oils Should You Avoid When Cooking?
The dark side of cooking oils lurks within refined seed oils. Their high content of linoleic acid, when consumed in excess, contributes to inflammation and metabolic disorders. Opting for alternatives like coconut, olive, or avocado oils can significantly improve your health.
The Hidden Truth: The Dangers Lurking in Vegetable Oils
Vegetable oils, often promoted for their affordability, can come at a cost to your health. Research reveals their link to chronic inflammation, which can pave the way for metabolic disorders. The choice of oil in your kitchen impacts your overall health, making it crucial to be mindful when making selections.
III. The Science Behind Oils and Health
Breaking Down Linoleic Acid: Its Impact on Health (*)
Linoleic acid, found abundantly in refined seed oils, has a detrimental effect on health. Excessive consumption can contribute to increased inflammation, leading to various metabolic disorders. Opting for oils with lower linoleic acid content can be a proactive step towards better health.
Investigating 4-Hydroxynonenal: How It Affects Our Bodies(*)
Scientific studies highlight 4-Hydroxynonenal's link to cellular damage, particularly in diabetic fat cells. These harmful effects are often attributed to the consumption of oils rich in linoleic acid, emphasizing the importance of choosing oils wisely to safeguard metabolic health.
IV. Spotting Unhealthy Cooking Oils: The Seven to Avoid
- Soybean Oil:
- Found in salad dressings, spreads, fries, and more, soybean oil, derived from GMO soybeans, dominates the market due to its low cost (*). However, it's about 55% linoleic acid, contributing to weight gain and inflammation. Its ultra-purified nature strips it of any meaningful nutritional value, making it best to avoid.
- Peanut Oil:
- Popular for frying due to its flaky texture and nutty flavor, peanut oil is rich in linoleic acid, linked to heart disease, diabetes, liver disease, and cancer(*). While it contains vitamin E, other sources like olive oil and avocados offer better alternatives.
- Corn Oil:
- Despite claims of lowering cholesterol, corn oil's high phytosterol content has its drawbacks. Elevated phytosterol levels correlate with increased heart disease risk and major coronary events(*)(*). Its 57% linoleic acid content further positions it as one of the least healthy cooking oils.
- Canola Oil:
- Though not the worst, canola oil still contains 28.1% PUFA, which is too high for consumption. While endorsed for reducing heart disease risk by the FDA due to its MUFA content, its reliance on phytosterols raises concerns. Additionally, the presence of erucic acid poses potential health risks.
- Cottonseed Oil:
- Despite its flavorlessness and use in high-heat cooking, cottonseed oil’s 55% linoleic acid content makes it a carrier of oxidized lipids, adverse for heart health.
- Sunflower Oil:
- Despite being marketed as a healthy choice, sunflower oil exceeds 60% linoleic acid and has shown significant DNA damage in studies compared to olive oil-rich feed, accelerating aging and increasing disease risks(*).
- Safflower Oil:
- Ranking as one of the worst vegetable oils with up to 70% linoleic acid, safflower oil's instability in high-heat cooking, lack of nutrients, and propensity to elevate inflammation and heart disease risk make it a definite no-go.
Steering clear of these unhealthy fats is key to supporting your keto lifestyle. Opt for healthier alternatives to ensure your keto journey remains successful and your health stays on point.
V. Practical Tips for a Healthier Kitchen
Good Fats: Coconut, Olive, and Avocado Oils Explained
Incorporating healthy oils into your diet is simpler than you think. Coconut oil adds a delightful taste to stir-fries and baked goods. Olive oil elevates salads and marinades. Avocado oil stands as a versatile choice for high-heat cooking due to its high smoke point. Embracing these good fats can transform your cooking experience.
Smart Swaps: Alternatives to Refined Seed Oils
When selecting oils for your meals, consider healthier alternatives like coconut, olive, or avocado oils. Making this simple switch can significantly reduce inflammation and support metabolic health, aligning perfectly with a ketogenic diet's principles.
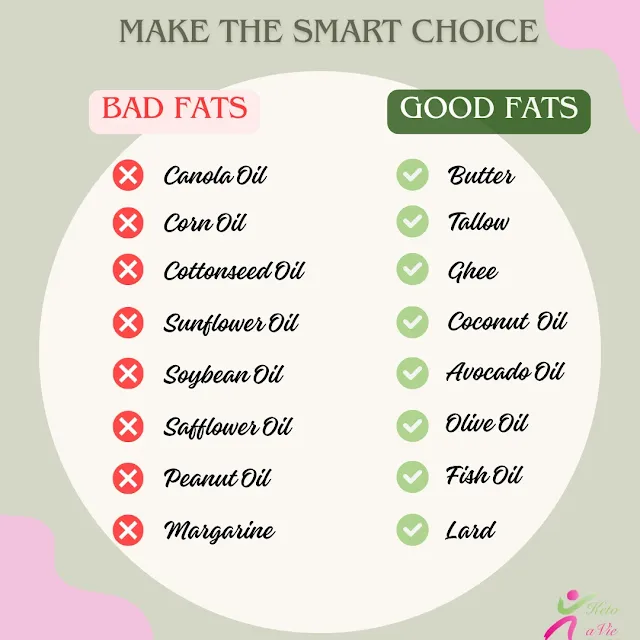
VI. Understanding the Difference: Choosing Healthy Fats
Navigating the world of fats is essential on your keto journey. Here’s a list of healthy cooking oils and good fats that align perfectly with your keto goals:
- Coconut oil
- MCT oil
- Avocado oil
- Extra virgin olive oil
- Butter
- Ghee
- Lard
- Cream cheese
- Heavy cream
However, not all fats are created equal. It's crucial to know which oils and fats to avoid to keep your keto journey on track. Here’s a list of oils and fats that should be avoided completely:
- Canola Oil
- Corn Oil
- Soybean Oil
- “Vegetable” oil
- Peanut Oil
- Safflower Oil
- Cottonseed Oil
- Grapeseed Oil
- Margarine
- Shortening
- Any fake butter or vegetable oil products
Putting what you've learned into action is awesome! Try out some super easy recipes using oils that are great for keto, like coconut, olive, or avocado oils. These recipes are tasty and keep your keto journey on track. Embrace those good fats in your cooking adventures!
VII. Conclusion: Navigating Healthy Oil Choices
Understanding the impact of cooking oils on inflammation and metabolic health empowers us to make informed choices. Opting for coconut, olive, or avocado oils over refined seed oils aligns with a ketogenic lifestyle, supporting metabolic health and combating inflammation.
As you embark on this culinary journey, remember, the small change of swapping oils can yield significant health benefits. Let's embrace a healthier future by choosing the right oils for a vibrant and well-nourished life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What oils are unhealthy to cook with?
Q2: Why does vegetable oil go bad?
Q3: Is vegetable oil healthy?
Q4. What are the health benefits associated with monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs)?
Q5. Why should certain oils and fats be avoided in our diet?
Q6. What are some common processed foods that contain unhealthy oils?
Q7. Is Palm Oil Healthy?
A: Palm oil is a controversial fat. It’s rich in saturated fats and stable at high heat, making it a common choice in food processing. Unrefined red palm oil contains beneficial antioxidants like vitamin E (tocotrienols) and beta-carotene (*), which can support cardiovascular and skin health. However, most palm oil in processed foods is refined and stripped of nutrients (*), often sourced unsustainably, contributing to deforestation.
Health impact: When consumed in moderation and in unrefined form, palm oil may be neutral or mildly beneficial. However, refined palm oil (often listed as "vegetable oil" on labels) is best avoided due to its pro-inflammatory potential and poor omega-6:omega-3 ratio.
Q8. What About Mustard Oil – Is It Safe and Healthy?
A: Mustard oil is widely used in Indian and Middle Eastern cuisine. It is rich in monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFA)and contains omega-3 fatty acids, both of which support heart health and reduce inflammation. It also contains allyl isothiocyanate (*), a compound known for its antimicrobial properties.
Important note: In some countries, pure mustard oil is labeled “for external use only” due to its high erucic acid (*)content, which in animal studies has been linked to heart muscle damage. However, human studies are less conclusive, and traditional use in cuisines has not shown widespread harm.
Recommendation: Use cold-pressed, food-grade mustard oil in moderation. It can be a healthy choice, especially when part of a traditional, whole-food diet.
Q9. What About Sesame Oil – Is It Safe and Healthy?
A: Yes, sesame oil can be a healthy choice when used mindfully. It's rich in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, contains antioxidants like sesamol and sesamin, and has anti-inflammatory properties(*). In traditional diets (especially in Asian and Middle Eastern cuisines), it’s been used for centuries both in cooking and therapeutically.
However, a few notes:
- Cold-pressed or toasted sesame oil is best used for low to medium-heat cooking or as a finishing oil to preserve its nutrients.
- Refined sesame oil may lose some of its antioxidants during processing and can be more prone to oxidation.
- It does contain some linoleic acid (around 40%), so while it’s better than many seed oils, it’s still best used in moderation, especially if you're managing inflammation or following a ketogenic diet.
Summary: Use sesame oil occasionally, ideally cold-pressed or toasted, and combine it with a base of healthier fats like olive, avocado, or coconut oil in your routine.
Q10: What About Grapeseed Oil – Is It Healthy?
Grapeseed oil is often marketed as a "heart-healthy" option, but the science tells a different story. While it does contain some vitamin E and has a high smoke point, it’s also extremely high in linoleic acid (around 70–75%), a polyunsaturated fat that becomes unstable when heated.
Excessive linoleic acid intake is linked to inflammation, oxidative stress, and metabolic dysfunction, especially when used frequently in cooking. Research also suggests that high dietary intake of linoleic acid may contribute to chronic diseases like obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular issues (*).
Additionally, grapeseed oil is often extracted using chemical solvents like hexane, which may leave residues and further degrade the oil's nutritional quality.
Bottom Line: Grapeseed oil is not the healthiest option. It's best to limit or avoid it, especially for cooking. Instead, opt for stable, nutrient-rich oils like olive oil, coconut oil, or avocado oil that support metabolic health and reduce inflammation.
Q11: What About Rice Bran Oil – Is It Healthy?
A: Rice bran oil is often promoted as a “heart-healthy” option due to its content of vitamin E (especially tocotrienols) and plant sterols. It also contains both monounsaturated fats (about 5g) and polyunsaturated fats (about 5g) per tablespoon. However, the balance of these fats is important to consider.
The concern lies in its high omega-6 (linoleic acid) content, which makes up nearly 35–40% of its fatty acid profile. While omega-6 fats are essential in small amounts, excess intake—especially without enough omega-3s—has been linked to:
- Chronic inflammation
- Oxidative stress
- Insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes
- Increased risk of cardiovascular disease
- Higher cancer and asthma risk in some populations
Additionally, rice bran oil is often chemically refined, using solvents like hexane, and then bleached and deodorized — processes that may strip away beneficial nutrients and increase oxidation risk, especially at high heat.
📲 Ready to Go Deeper? Your Next Step Starts Here
If you're thinking, "This is exactly what I'm struggling with," you're not alone—and you're in the right place.
Whether you're dealing with stress, insulin resistance, stubborn weight, hormonal imbalances, or low energy, I’m here to help you create a clear, personalized path forward. Together, we can rebalance your hormones and restore your energy, clarity, and confidence.
🔥 Try My 7-Day Keto & Intermittent Fasting Trial
This structured mini-program is designed to help you kickstart fat burning, reduce sugar cravings, and stabilize your blood sugar naturally.
Here’s what you’ll get:
✅ A simple, easy-to-follow 7-day meal plan
✅ Practical fasting tips that work for real life
✅ Daily guidance to stay in ketosis
✅ Personalized support & progress tracking
👉 Click here to start your 7-Day Keto Trial and take the first step toward sustainable healing and transformation.
📘 Your Practical Guide to Insulin Resistance & Hormonal Balance
Struggling with energy crashes, period problems, or weight that won’t budge?
I created a comprehensive digital guide just for you—especially if you're a woman dealing with metabolic dysfunction or estrogen dominance.
What’s inside:
✔️ A fully structured 30-day plan
✔️ Food, mood & digestion tracking sheets
✔️ Weekly meal plans and keto shopping lists
✔️ Exclusive educational videos
✔️ Tools to overcome keto flu and stay motivated
🛒 Get your copy now or find it through my bio on Instagram: @ketoavie
🎯 Real change starts with one small step—this is yours.
Let’s take it together.
💌 Contact: info@ketoavie.se
🌐 Website: www.ketoavie.se
📲 Instagram: @ketoavie
📘 Facebook: Ketoavie
🛒 My Favorite Wellness Picks
💚 Save on supplements: Use iHerb code DWN2454 at checkout
🛍️ Browse my top products: Amazon Favorites




Comments
Post a Comment